DHCP is one of those things that we all take for granted every single day, If one day DHCP just got up and left, that would be pretty bad.
DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol its goal is to assign a unique IP Address to our host it also provides other network addresses such as the subnet mask, default gateway, and the DNS Address come in two flavors it comes as a client and as a server. Let’s see an Example
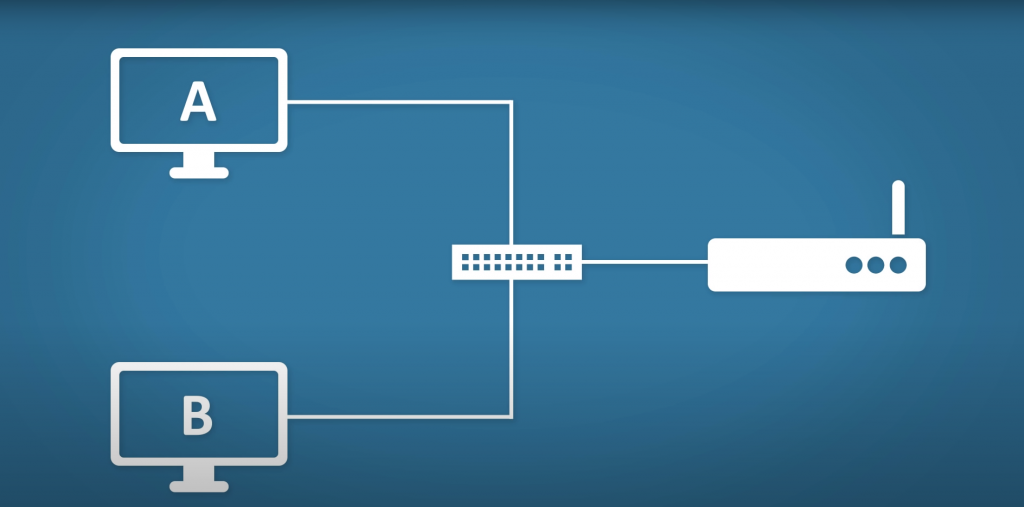
Here is our network we have two computers a switch and Router for our computer to work on our network. They need an IP Address not just any IP Address that address has to be unique on the network otherwise data goes to host A when it should actually be going to host B, host A doesn’t know what is going on and the whole thing becomes a mess. We could assign these addresses manually, We only have two computers, so it wouldn’t be hard but imagine if we have three hundred plus computers this could be so challenging, We really don’t want to be doing that, So how does DHCP sort this out.?
Each computer will run a DHCP client and this will allow the computer to ask for an IP Address somewhere on the network there will be a DHCP server. This is where the IP Addresses are managed DHCP Server can be run on Routers or Servers. At your home is likely built into your router but in an enterprise network, it is likely handled by a server,
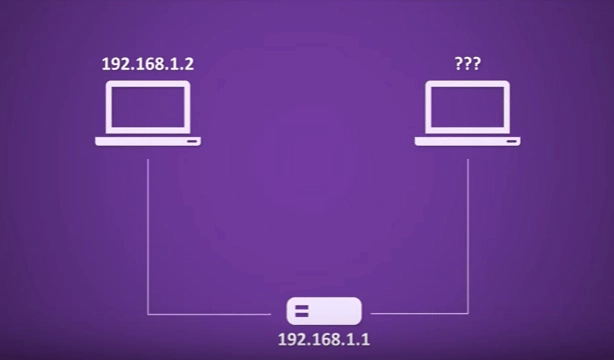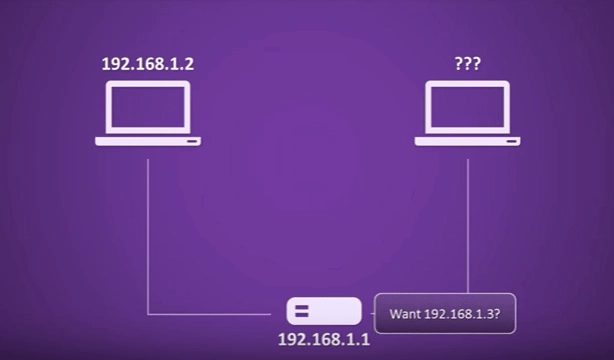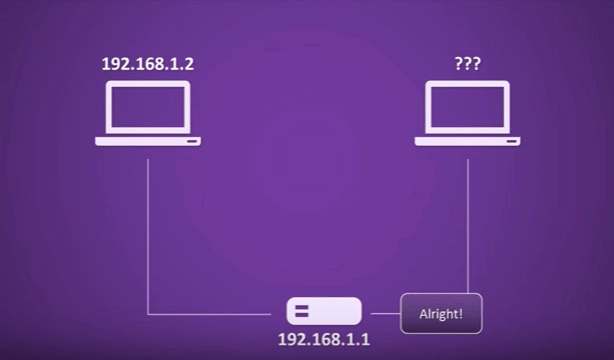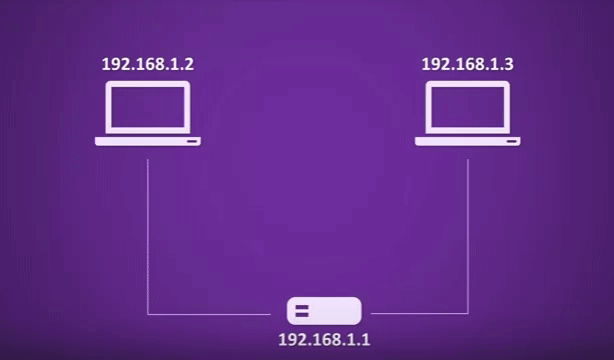
Step One: DHCP Discovery
When a device joins a network, it broadcasts a DHCP discovery message, known as a DHCPDISCOVER, to request an IP address from a DHCP server. This message is typically sent as a broadcast on the local network, and it contains the device’s MAC address.
Step Two: DHCP OFFER
When a DHCP server receives a DHCPDISCOVER message, it checks its pool of available IP addresses and configuration settings. If an IP address is available, the DHCP server constructs a DHCP offer message, known as a DHCPOFFER. This message contains the IP address being offered, as well as other network configuration parameters such as subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server addresses. The DHCPOFFER message is then broadcasted to the requesting device.
Step Three: DHCP Request
Upon receiving one or more DHCPOFFER messages, the requesting device selects one of the offered IP addresses and sends a DHCP request message, known as a DHCPREQUEST. This message is sent as a broadcast and includes the selected IP address.
Step Four: DHCP Acknowledgement
When the DHCP server receives a DHCPREQUEST message, it verifies the requested IP address’s availability and uniqueness. If the IP address is still available, the DHCP server sends a DHCP acknowledgment message, known as a DHCPACK, to the requesting device. The DHCPACK message confirms the allocation of the IP address and includes the lease duration, which specifies how long the device can use the assigned IP address.
Study Notes.
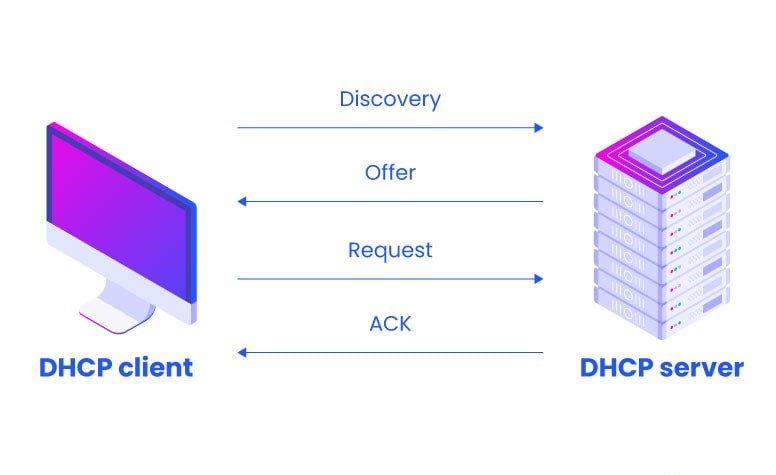
DHCPDISCOVER -> Looks for a DHCP Server
DHCPOFFER -> The DHCP Server offers an address
DHCPREQUEST -> The host requests to lease the address
DHCPACK -> DHCP Server sends an IP Address to the host
DHCP Server works on Port 67
So life without DHCP isn’t worth thinking about pretty much everyone uses it every single day without giving it a second thought.
As always, we would like to know your thoughts in the comments box. Don’t forget to share this with your friends.